Module 4: Methods of Information Collection - Section 2:3
2.3 Error
 When we measure something or collect information, there are many reasons that our findings might be wrong. The most obvious reason is that we could simply make a mistake in writing something down. This kind of mistake is how we might usually think about error. However, there are other kinds of errors that we might not see unless we knew to look for them. These errors are not mistakes in the sense that we have done something wrong. These types of errors can decrease the reliability or accuracy of what we do, but often because of things that we cannot control.
When we measure something or collect information, there are many reasons that our findings might be wrong. The most obvious reason is that we could simply make a mistake in writing something down. This kind of mistake is how we might usually think about error. However, there are other kinds of errors that we might not see unless we knew to look for them. These errors are not mistakes in the sense that we have done something wrong. These types of errors can decrease the reliability or accuracy of what we do, but often because of things that we cannot control.
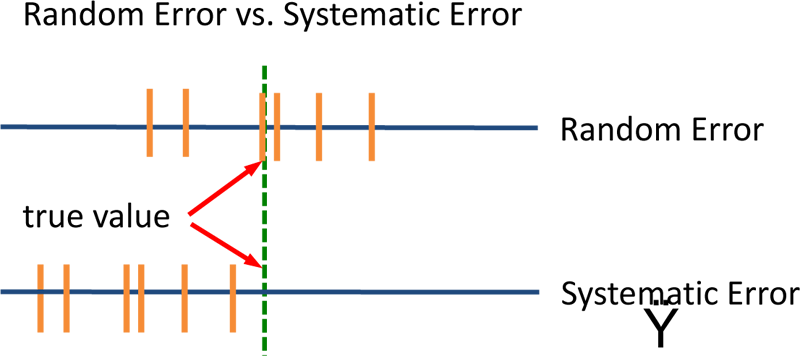
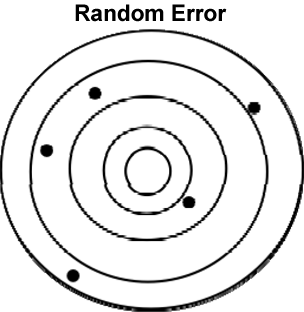 One of these is called Random Error. An error is considered random if the value of what is being measured sometimes goes up or sometimes goes down. A very simple example is our blood pressure. Even if someone is healthy, it is normal that their blood pressure does not remain exactly the same every time it is measured. If several measurements of blood pressure were taken over time, some would be higher and some would be lower. The reason for this random error is to be expected because of variation in normal processes in the body and in the way that the measuring device works. If error is truly random, and if we take enough measurements, then it is still possible to get a good estimate of what we are measuring. However, if random error is large, then our measurements will be unpredictable, inconsistent and they will not represent the true value of what we are measuring.
One of these is called Random Error. An error is considered random if the value of what is being measured sometimes goes up or sometimes goes down. A very simple example is our blood pressure. Even if someone is healthy, it is normal that their blood pressure does not remain exactly the same every time it is measured. If several measurements of blood pressure were taken over time, some would be higher and some would be lower. The reason for this random error is to be expected because of variation in normal processes in the body and in the way that the measuring device works. If error is truly random, and if we take enough measurements, then it is still possible to get a good estimate of what we are measuring. However, if random error is large, then our measurements will be unpredictable, inconsistent and they will not represent the true value of what we are measuring.
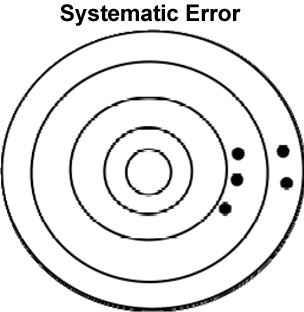 The second type of error is called Systematic Error. An error is considered systematic if it consistently changes in the same direction. For example, this could happen with blood pressure measurements if, just before the measurements were to be made, something always or often caused the blood pressure to go up. Or this could happen because our device for measuring blood pressure was defective so that it always gave a result higher, or always gave a result lower, than the true value. In these cases, even if our measurements were predictable and consistent, the results would still not be accurate.
The second type of error is called Systematic Error. An error is considered systematic if it consistently changes in the same direction. For example, this could happen with blood pressure measurements if, just before the measurements were to be made, something always or often caused the blood pressure to go up. Or this could happen because our device for measuring blood pressure was defective so that it always gave a result higher, or always gave a result lower, than the true value. In these cases, even if our measurements were predictable and consistent, the results would still not be accurate.
Definition: Error in research is anything that interferes with making a confident conclusion about the study.
Case Examples for Systematic and Random Error
Systematic Error
In a study on weight loss, researchers determined at the end of the study that the scale that was used to measure participant’s weight was inaccurate. The scale added 10 pounds to the person’s actual weight every time the scale was used. Because the researcher realized that the scale consistently added ten pounds to each participant’s weight, they adjusted for this problem when analyzing the results.
Section 2.3: Discussion Questions
- If you were the researcher, how would you handle this problem if you found out about it at the end of the study?
- What are some things the researcher should have done in the first place to avoid this problem?
- Is systematic error problematic in research in general if it can be corrected? What if the researcher doesn't know about the systematic error?
Random Error
In a study on weight loss, a scale was used that added a few pounds more or a few pounds less each time the scale was used. The researcher did not know that the scale did not measure the participant’s exact weight. Because the researcher did not realize this, the researcher could not adjust for this problem when analyzing the results. This caused the study results to include some error.
Section 2.3: Discussion Questions
- Are the results of this study accurate? Why or why not?
- Does the use of a slightly inaccurate scale cause serious problems with the study results?
- Is there anything that the researcher should have done to avoid this problem?
- Which do you think is a more serious problem in research – systematic or random error?
- Which type of error – random or systematic - is easier to control?





