Module 3: Elements of Research - Section 3
Section 3: Sampling
Sampling is the process of choosing participants for a research study. Sampling involves choosing a small group of participants that will represent a larger group. Sampling is used because it is difficult or impractical to include all members of a group (e.g., all Latina women in the United States; all male college athletes). However, research projects are designed to ensure that enough participants are recruited to generate useful information that can be generalized to the group represented.
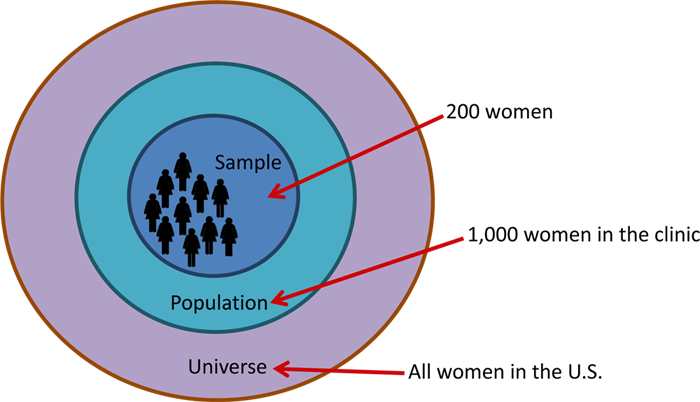
Definition: Sampling is defined as the method by which some members of a larger group are selected. The usual goal is sample those members so that they are representative of the group as a whole.
Case Example for Sampling
An investigator will be studying nutrition among Latina women. To find participants to interview, she requested a list of names and contact information for all Latina women from a community clinic. These women had already provided consent and had agreed to be contacted about participating in future research studies. The list included 1,000 names of potential participants for the nutrition study. The investigator chose 200 of the women from this list to contact for possible inclusion in the study.
Section 3: Discussion Questions
- What is the purpose of selecting a smaller group of participants from a larger group?
- Do the women included on this list represent the larger group?
- Would you choose participants differently if this was your study? If so, how would you do it?
- What would happen if the investigator chose individuals from the list that she knew? Would this affect the results of the study?





